Quality risk management is a systematic, risk-based approach to quality management. The process is composed of the assessment, control, communication, and review of quality risks. It is especially critical in the pharmaceutical industry, where product quality can greatly affect consumer health and safety.

Why quality risk management is important?
Quality risk management has become an integral part of the quality assurance and control system. When you will start practicing risk management philosophy, tools and techniques you will find your decision-making process has significantly improved. So does your level of compliance.
Risk management will provide you with a tool of a systematic approach to making prudent risk-based decisions in the following areas of activities:
– During the validation approach and testing
– Qualification of equipment, facilities, and utilities
– Impact assessment of new computerized systems
– During the determination of external suppliers & procurement of materials
– Efficient deviation investigation, change management, and customer complaint handling
– Determination of external & internal audit frequency
– Critical instrument calibration frequency
– Risk-based environment, health, and safety management
– Distinguishing deviations events
– Improving overall regulatory compliance, etc.
Quality risk management involves the art and science of identifying, analyzing, assessing, and managing uncertain events.
Events that can impact product quality or compliance with registered dossier throughout a product’s life.
It requires a balanced approach, weighing the costs of avoiding threats or enhancing opportunities and the benefits to product quality that can be gained.
It supports more effective and consistent risk-based decisions and makes the decision-making process more transparent.
What is quality risk management in pharmaceutical?
According to FDA Guidance for Industry – Q9 Quality Risk Management, “Quality risk management is a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality of the drug product across the product lifecycle.
With product lifecycle, we can include the impact on the quality, safety, or efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Put simply that any action, environment, process, system, personnel, facilities, and equipment that are involved in making pharmaceutical products can introduce risk to product quality. And quality risk management is the only proven way to identify those risks early and control them effectively. So that the potential impact on product quality would be minimal.
The essence of quality management is risk management. All activities that are undertaken during quality assurance in pharmaceutical operations are to minimize risks. So that you can deliver your promise to supply medicinal products that are safe, pure and effective for human use.
Risks are also called hazards that may arise every aspect of a process. Once you can identify a risk, you should analyze that against the attributes such as likelihood and consequence.
You ask the question to your audience in case the failure of a risk what would the consequence be on product quality? And also what would be the likelihood of such failure to occur?
Don’t be fooled by different risk management terminologies. Some organizations will call consequence as severity and likelihood as probability. These terms are interchangeable without the loss of any meaning.
You should also consider what control mechanisms are in place to prevent such failure in the future. If the control is found inadequate to mitigate the risk, you must consider new controls to implement. In most cases, these questions need to be asked before a risk event would potentially occur. Not after.
A quality risk assessment is a team effort where the subject matter experts are gathered to brainstorm every possible risk question at length. The team together assigns a rating on the consequence if failure of risk would occur and the probability of such an incident to occur.
The ratings could be qualitative such as high, medium or low. Sometimes, ratings are quantitative. We will talk about the ratings more broadly in the later part of the post.
Anyway, by the end of a quality risk management exercise, each individual risk area is assigned a risk pro between high, medium, and low. Existing controls are also identified and recorded during this process.
If the team finds the existing controls are inadequate to minimize the risk, a proportionate risk treatment plan must be created to minimize, eliminate or transfer the residual risk.
A risk treatment plan lists a group of additional actions to be taken during the life of the contract to control the risks.
If the risks appear to be an opportunity instead, you will make every effort to take the most benefit out of it.
What is quality risk management framework?
According to the ICH Q9 guideline, the risk assessment process itself includes the identification of hazards (risk events), analysis of those hazards by throwing every possible risk question to dissect completely and evaluation of hazards by rating the potential consequences (severity) and likelihood (probability) of failure.
Risk controlling also has the decision-making components such as what do you do with those risks? Will you take mitigation activities? Or you might have the appetite or reason to accept the risk like business as usual.
A generic quality risk management process flow looks like the following image:
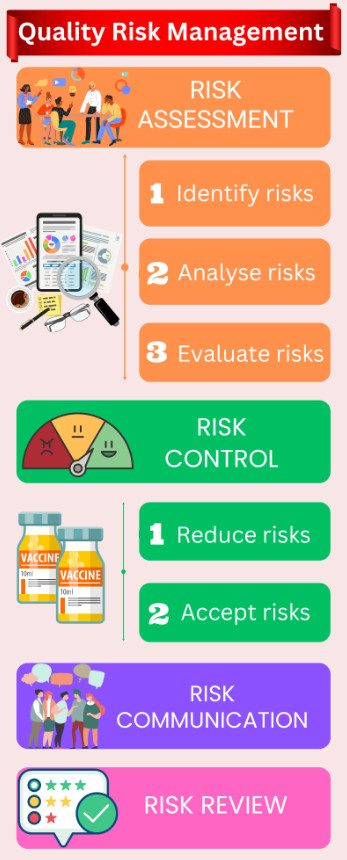
Summary
Quality risk management in pharmaceutical is a systematic process for the assessment, control, communication and review of risks to the quality of the drug product across the product lifecycle.
Quality risk management has become an integral part of the quality assurance and control system in the pharmaceutical industry. When you will start practicing risk management philosophy, tools and techniques you will find your decision-making process has significantly improved. So does your level of compliance.

GMPc Vietnam is recognized throughout Vietnam as the leader in providing turnkey consulting solutions for GMP-certified facility projects, including Pharmaceuticals, Cosmetics, Health supplements and Veterinary pharmaceutical. Though 12 years of development 2011 to 2023, GMPc has implemented more than 230 GMP-certified facility projects, equaling to more than 80% of market share of the field in Vietnam. Not only do domestic customers, foreign investors also choose GMPc as their consultant when investing new factories in Vietnam, such as Kyoto Biken Vaccine Factory, Nippon Chemiphar Pharmaceutical Factory, Shimizu Contractor, Kajima Contractor, etc.
Consulting services for EU GMP
Consulting services by GMPc Vietnam
GMP project consulted by GMPc Vietnam


